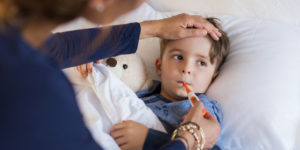
A child’s health is instrumental to their growth and development which is why it is important to make sure you start doing things like taking your child to the dentist at an early age and making sure they understand the importance of healthy living . As children’s immune systems are not fully developed, they are often prone to infections and illnesses; the most common illnesses amongst children are outlined below:
Coughs and Colds
Coughs and colds are common amongst children due to their vulnerability to infection because of their weaker immune system. Coughs and colds are highly contagious and are constantly passed around children in nurseries, schools and colleges. Symptoms often include a high temperature, nausea, aches and pains. It is important to check your child’s temperature regularly if they are suffering from a cold; a child’s temperature should be 38 degrees; if it goes significantly higher than this you should seek medical help. Generally, most children recover fairly quickly from coughs and colds; you should ensure they have plenty of fluids and lots of rest; it may also be beneficial to give them over the counter pain relief but you should check the labels carefully or seek help from a pharmacist or doctor prior to administering the medication.
Asthma
Asthma is increasingly common in young children and can cause the chest to tighten causing difficulty with breathing and wheezing. Mild asthma can usually be treated with occasional doses of medication while severe asthma usually requires regular medication; most severe asthma sufferers carry inhalers around with them at all times. Many children grow out of asthma although some will suffer for life. It is important to get your child diagnosed if you feel they may be suffering from asthma; this will ensure they have the medication they need; asthma attacks can be very dangerous and potentially fatal.
Meningitis
Meningitis is an extremely serious condition and should be treated immediately. Meningitis affects the brain and spinal cord and can cause permanent damage. Symptoms often include many of those which present when an individual is suffering with a heavy cold; however there are certain symptoms which are more severe and point to a more serious infection such as meningitis.
There are two types of meningitis; these are bacterial and viral; symptoms are similar for both however bacterial meningitis is often more serious and should be treated as quickly as possible. The most common symptoms in children include a soaring temperature, vomiting and loss of appetite, prolonged crying, pain in the legs and hands and cold hands or feet; children may also turn pale and may develop blotchy skin; if the skin turns blotchy you should place a glass on the surface; if the rash does not change colour or fade you should seek emergency medical help. Babies with meningitis may also get a swollen fontanel. It is often difficult to determine which form of meningitis your child is suffering from symptoms alone so you should seek emergency medical help in all cases.
Eczema
Eczema is a skin condition, which is common in young children; often it is characterised by patches of irritated, dry, red skin and can be very itchy. Eczema can commonly be treated by using a variety of lotions, creams and bath soaks; these help to ease itchiness and irritation. Most children grow out of eczema.
Vomiting and diarrhoea
Vomiting and diarrhoea are fairly common in children because their immune systems are not fully developed and they are consequently prone to catching infections. Usually these infections only last a short period of time. There is generally no specific treatment for these illnesses but you should be aware of any changes in your child’s temperature and ensure they have plenty of fluids; this will prevent them from becoming dehydrated.
Chickenpox
Chickenpox is most common in children and is highly contagious. Chickenpox is generally very easy to diagnose as it is characterised by the development of small red spots all over the body; these spots are usually very itchy but you should try to discourage your child from scratching as this may lead to scarring. There are lotions available to ease itchiness and swelling. If your child has chickenpox you should ensure they remain at home in order to prevent passing it on to other people; your child will be contagious until approximately one week after the spots first appear; they should have scabbed over by this time. Children may feel very poorly with chickenpox; they may have a high temperature, be clingy and feel emotional.
Child obesity
Child obesity is steadily increasing right across the Western world as children do less exercise and eat more processed foods, which are high in fat and salt. You should try to limit the amount of fatty and sugary foods your child eats; these foods have no health benefits and may cause long-term illnesses if your child gains a lot of weight. Home cooking is often much healthier as you can control what you put in the food; many ready meals have artificial ingredients which may be harmful if eaten regularly. Try to encourage your child to get outdoors and do some exercise; this can involve going to the park, doing an activity such as swimming or ballet or playing a team sport for example.
